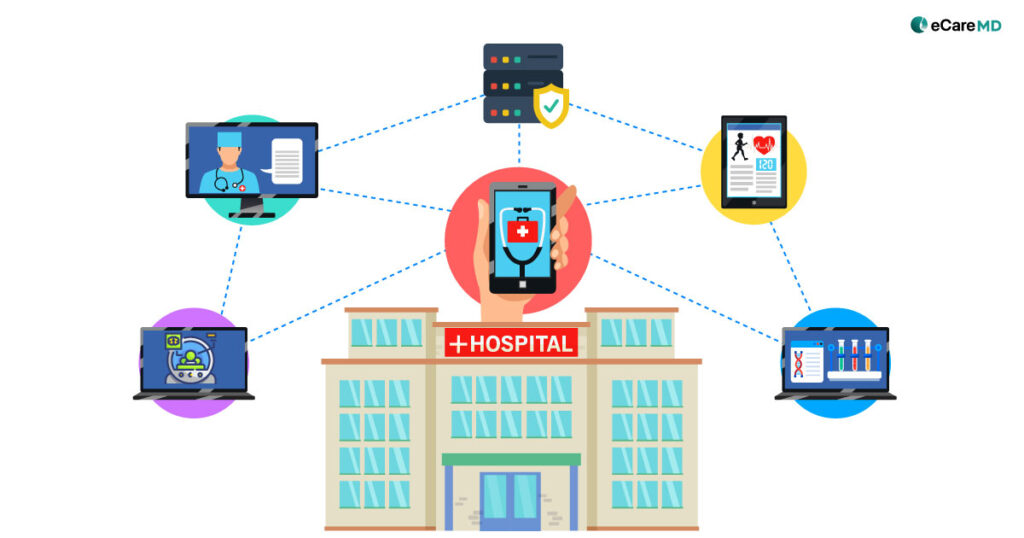
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services aka CMS RPM Program has initiated data-driven healthcare practices to mainstream. This has not only increased the efficiency of the practice but also has had a huge impact on the patient’s health outcomes, especially for chronically ill patients.
However, as RPM deals with collecting, monitoring, and transmitting sensitive patient information, safeguarding it with appropriate healthcare compliance and security measures is necessary. It is important to secure healthcare data to maintain transparency in the process and protect patient’s health information.
Leaks of patient data can lead to heavy fines and damage your practice’s reputation. To overcome this, CMS has introduced several guidelines for RPM programs for patient data protection.
In this blog, we will understand the security and compliance of the CMS RPM program and how to secure patient data in CMS RPM.
The data that RPM devices will be transmitted to the providers’ system will contain crucial records of patients’ vitals. This is sensitive data, and protecting it is one of the fundamental rights that healthcare providers must adhere to.
The consequences of such data breaches and theft can be severe for both the patients’ and the providers’ practice. While the integrity of the practice is questioned, it also reduces public trust in healthcare.
Data breaches and thefts can lead to privacy violations and psychological distress and disrupt healthcare access. On the other hand, for providers, it leads to financial loss, complex legalities, disruption in operations, and reputational harm.
That is why healthcare data protection is very important. It not only helps in gaining patients’ trust but also assures them that transparency in care delivery is maintained.
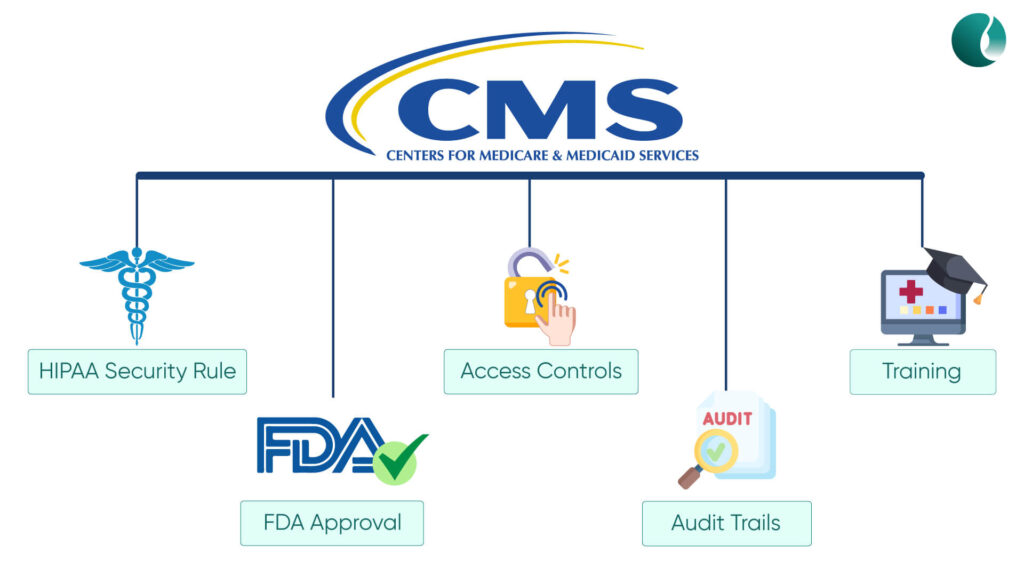
The CMS, with regard to patient data protection, security and privacy in remote patient monitoring programs, has established various regulations for its safeguarding. In an attempt to build a safe and secure digital healthcare ecosystem, here are some of the key regulations that CMS encourages to follow:
1.HIPAA Security Rule: The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act is the cornerstone of protecting PHI in healthcare. CMS requires your RPM program to get HIPAA compliance as it mandates risk assessments, administrative safeguards, physical safeguards, and technical safeguards.
2. FDA-approved RPM Devices: CMS requires and encourages the use of FDA-approved RPM devices in your RPM program. This ensures the safety and usability of the devices.
3. Access Controls: CMS requires you to establish and enforce access controls to ensure authorized access to patient data.
4. Audit Trails: Implement audit trails to track and monitor the access to patient data. This will help in detecting and addressing any unauthorized activities.
5. Training and Awareness: CMS also encourages training and awareness of both the patients and providers CMS RPM security. Also, it emphasizes providing hands-on training on RPM software, processes, and devices.
1. Weak Authentication and Authorization: Insecure login details and weak authentication can lead to improper access control, leaving loopholes and unauthorized access to sensitive data.
2. Unencrypted Data Transmission: Transmitting sensitive patient data over unsecured networks without encryption makes the system vulnerable to interception and data theft.
3. Vulnerable Device Software: Outdated remote patient monitoring device firmware and software can lead to various flaws in the system that can be easily exploited, compromising the CMS RPM security measures.
Apart from these, ensuring mobile application and cloud storage can leave the entire RPM system at a high risk of security. That is why it is important to build a robust ecosystem with strong encryption to maintain the security of the RPM program.
Remote monitoring devices are what bring meaning to your remote patient monitoring program. Ensuring secure integration of the devices in the RPM systems ensures the quality of the devices and ensures patient health information.
Some of the most common CMS RPM program guidelines to follow in this are:
1. FDA Approval: Remote patient monitoring devices must be FDA-approved to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
2. Patient Consent:Patient consent is required not only to enroll in the RPM Program but also to use the RPM devices.
3. Physician Order: A physician’s order is required for the patient to qualify for the RPM program and to use RPM devices.
4. Data Collection and Transmission Capabilities: The RPM devices need to be capable of collecting patients and transmitting them to the provider’s system.
5. Device Security: The device must have robust security measures like strong encryption, access control, audit trails, and regular updates for patient data protection.
6. Security Compliance: The RPM devices must adhere to the privacy and security regulations set forth by HIPAA and other regulatory bodies.
Along with that, the cloud storage for the data collected by the RPM devices also complies with the CMS guidelines to safeguard patient health information.
Secure data transmission and storage simplifies the process of secure data transmission. The transmitted data is often sensitive in nature and can reveal a lot about the patient. Furthermore, unauthorized access to crucial patient data can disrupt the workflow of the practice and put the patient at risk.
Implement robust encryptions for healthcare data protection to be transferred in a secure ecosystem. This also addresses the issue of unauthorized access and increases the security of the patient data when it is at rest.
Also, being a provider ensures that the patient data is stored on secure cloud storage. This adds another level of CMS RPM security to access data, and it also brings the flexibility factor in accessing data for both patients and providers.
As said earlier, patient consent is important for enrolling the patient in the RPM program and also for using the RPM devices. However, getting patient consent is and will always be a challenge for providers. One of the best ways to get consent is by effective communication. Educate patients about the patient data security measures and how they can help them in improving their health.
It is important to obtain patient consent for data collection and transmission as CMS recognizes this as a crucial step for reimbursement and insurance claims.
During the CMS RPM program integration, establish clear and secure communication channels to address patient concerns. As it encourages patient engagement, patients can stay connected with providers and work together for a common goal to improve health outcomes.
However, one thing to remember about patient consent is that the patient should give consent either in writing or verbally.
CMS has set some healthcare data protection security protocols that must be followed to ensure the CMS RPM security of patient information. As there are a lot of things like RPM devices, software, CPT codes, etc., are involved, staff training on patient data security is necessary.
Provide all the necessary means to provide the healthcare staff with hands-on experience with the RPM system. Along with that, CMS regularly updates its guidelines and compliance requirements. With regard to this, you and your healthcare staff need to be updated with the changes.
Also, while providing hands-on training with the RPM system, make sure that you conduct simulated security drills so that staff is aware of the requirements. After all, the healthcare staff are humans and can make honest mistakes. To avoid that, preparing them with training can help you minimize the risk and ensure data security.
The success of your CMS RPM program depends on the collaborative efforts of you and your vendor. When consulting a third-party vendor, verify the security measures that they take to ensure patient data protection, safety and CMS RPM security.
Assess the healthcare compliance of the external partners with the CMS regulation. Oftentimes, you reach out to third-party vendors for RPM devices and RPM software development and maintenance. Here, you need to ensure your vendor follows all the CMS RPM security like HIPAA compliance, FDA-approved devices, etc.,
To keep your practice safe from some legalities, ensure that your contractual agreement with the vendor includes healthcare data protection provisions. This safeguards your program from data breaches and other threats.
The healthcare industry is a crucial element of the ecosystem, and moving toward the digital landscape, it is prone to cyber-attacks and threats. Though following the security measures and compliances mentioned above in the article can help you navigate through the process, it’s always better to develop a robust incident response plan.
Establish procedures for reporting any security incident in case of any mishaps so that you can take necessary action to protect your practice from such future incidents. Moreover, addressing any security threats in real-time and resolving security breaches.